An introduction to Solid State Modules
INTRODUCTION:
Generally speaking, the power module refers to the device mainly composed of power components (such as SCR, TRIAC, MOSFET, IGBT). Narrowly speaking, power modules are referring to solid-state modules to differentiate with solid state relays. The main function of the solid state relay is electronic switch, and the solid state module is used to adjust the load power, and voltage regulation.
Through this article you will learn: What are the power modules? What is the structure of the power module? How many types of the power module? How does the power module work? How to select the power module?
You can quickly navigate to the chapters you are interested in through the Directory below, and the Quick Navigator on the right side of the browser.
CONTENTS
§1. What is the Power Module? |
§2. How does the Power Module work? |
§3. How to select the Power Module? |
§1. What is the Power Module?
The Power Module (PM), also known as electronic power module, or solid-state power module, is a module that combines power electronic components into solid-state structure with a certain functional. Through the internal integrated circuit (IC), the power module can output the power and adjust the power of the load. According to the main functions, we divide solid-state modules into solid state voltage regulation modules and solid state rectification modules.
1.1 Solid State Voltage Regulation Module

The solid state voltage regulation module (also known as the solid state power voltage regulation module, the solid state power regulating module, the solid state voltage regulating module and the solid state power voltage regulator module) are used to adjust the voltage or power of the AC load. Generally, the solid state voltage regulation module is integrates the synchronous transformer, the power output circuit, the phase shift circuit, the detection circuit, and can be directly connected to the load to control it. Solid state voltage regulation modules are widely used into various fields, such as scientific research, experiment, detection, heating insulation, soft start.
The solid state phase-shift module (or solid state phase-shifting module) is a type of voltage regulation module, but it can only output a phase-shift signal and cannot be directly connected to the load. So, it requires a set of solid-state relays (or power thyristor circuits) and a synchronous transformer to achieve the voltage regulation function.
According to the phase, the solid-state voltage regulation module can be divided into: single-phase solid-state voltage regulation modules, and three-phase solid-state voltage regulation modules.
According to whether the loop is closed, the solid-state voltage regulation module can be divided into closed-loop type solid-state voltage regulation module and open-loop type solid-state voltage regulation module (unclosed-loop type solid-state voltage regulation module).
According to whether the weak current part is isolated from the strong current part, the solid-state voltage regulation module can be divided into full isolation type solid-state voltage regulation module and non-full isolation type solid-state voltage regulation module.
According to the number of controlled loads (channels), the solid-state phase-shift module can be divided into: single channel solid-state phase-shift module (or single phase solid-state phase-shift module), dual channel solid-state phase-shift module, three channel solid-state phase-shift module (or three phase solid-state phase-shift module).
According to the external power output device, the solid-state phase-shift module can be divided into: external solid state relay type phase-shift modules, and external thyristor power circuit type phase-shift modules.
1.2 Solid State Rectification Module
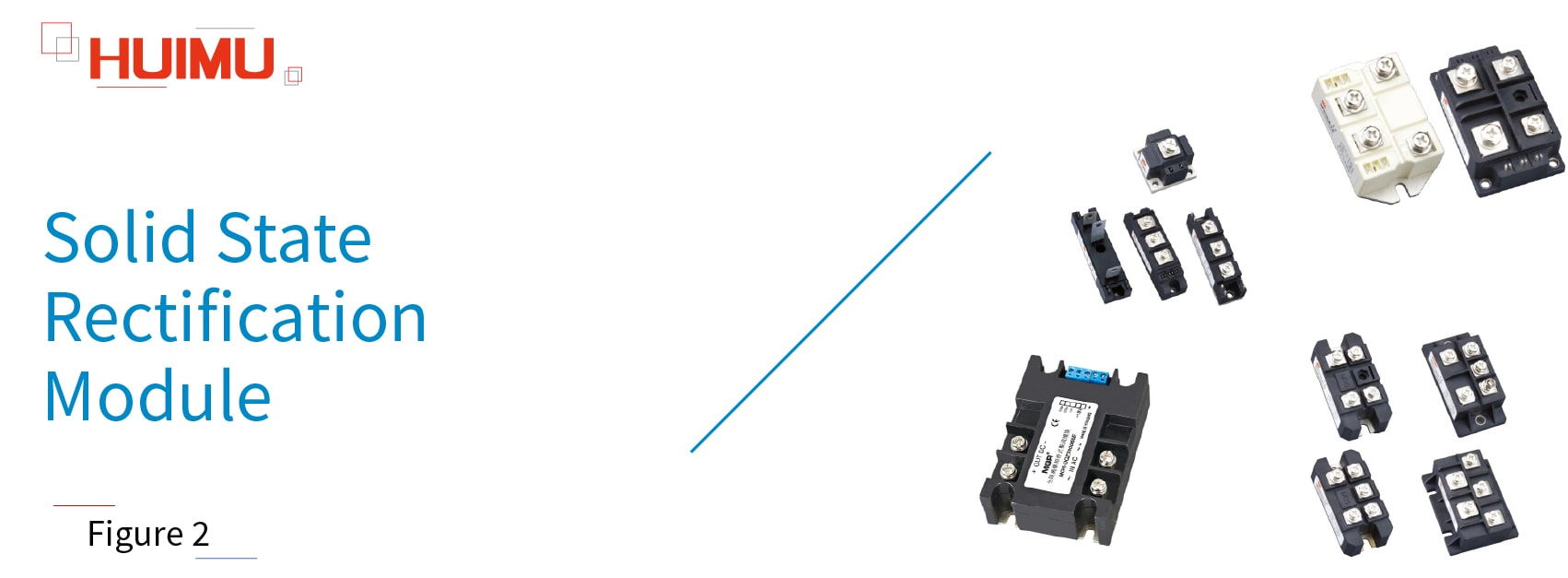
The solid state rectification module (or solid state rectifier module) uses power components (such as power diodes, power thyristors, rectifier bridges) to rectify Alternating Current (AC) into Pulsating Direct Current (Pulsating DC) or Rectified Alternating Current, whose direction (positive and negative direction) can not be changed, but their magnitude changes with time. It should be noted that, Solid State Diodes and Rectifier Silicon are uncontrollable devices, and Semiconductor Control Rectifier and Unidirectional thyristor are controllable devices. Solid state rectification modules are widely used in various fields, such as the DC power supply of instruments, the input rectified power supply of PWM inverter, the excitation power supply of DC motor, the input rectification system of switching power supply, the soft-start capacitor charging system, the electric drive and auxiliary current, the inverter welding machine, and the DC power charging system.
According to the phase, solid-state rectifier relays can be divided into: single-phase solid-state rectifier relays, three-phase solid-state rectifier relays.
According to the phase, solid-state bridge rectifiers can be divided into: single-phase solid-state bridge rectifiers, three-phase solid-state bridge rectifiers.
According to the number of rectifier silicon (or diode), solid-state rectifier modules can be divided into: half-wave rectification modules, full-wave rectification modules (half-bridge rectification modules), and full-bridge rectification modules. The half-wave rectification module has only one rectifier silicon (or diode), the full-wave rectification module (half-bridge rectifier module) has two rectifier silicon (or diodes), and the full-bridge rectification module has four rectifier silicon (or diodes). The full-wave rectification modules have the similar function as the full-bridge rectification modules, but the cost of the full-bridge type rectification module is higher than that of the full-wave type rectification module, and its requirements on the transformer are lower than that of the full-wave type rectification module.
According to whether the weak current part is isolated from the strong current part, solid-state rectification modules can be divided into full-isolation rectification modules and non-full-isolation rectification modules.
According to the combination of diodes and thyristors, solid-state rectification modules can be divided into uncontrolled rectification modules, fully-controlled rectification modules and half-controlled rectification modules. The output components of the uncontrolled rectification modules are completely composed of rectification diodes. The output components of the fully controlled rectification modules are composed of thyristors. The output components of half-controlled rectification modules are composed of diodes and thyristors.
§2. How does the Power Module work?
In this chapter you will learn how do electronic power modules work.
2.1 The Working Principle of Solid State Voltage Regulation Module
Take our MGR-DT series single phase voltage regulation module as an example. The MGR-DT series consists of a synchronous transformer, a phase detection circuit, a phase shift trigger circuit, and a thyristor output circuit. MGR-DT series has two kinds of control mode (automatic control and manual control). Automatic control mode, that is, the control signal applied to the solid-state voltage regulator is generated by PLC or computer system. And the automatic control mode has four kinds of control signal (0-5VDC, 0-10VDC, 1-5VDC, 4-20mA). Manual control mode, that is, the control signal (0-5VDC) applied to the solid-state voltage regulator is generated by manually controlling a potentiometer under the 5VDC internal power supply.
The wiring of MGR-DT series:
Ports 1 and 2 are the power output ports of the solid-state voltage regulation module, and the load and power supplier can be directly connected to them. The voltage and current of the inductive load are not synchronized, and will be charged and discharged during the power-on and power-off process, therefore, in order to facilitate the description of the working process, we will use a purely resistive load.
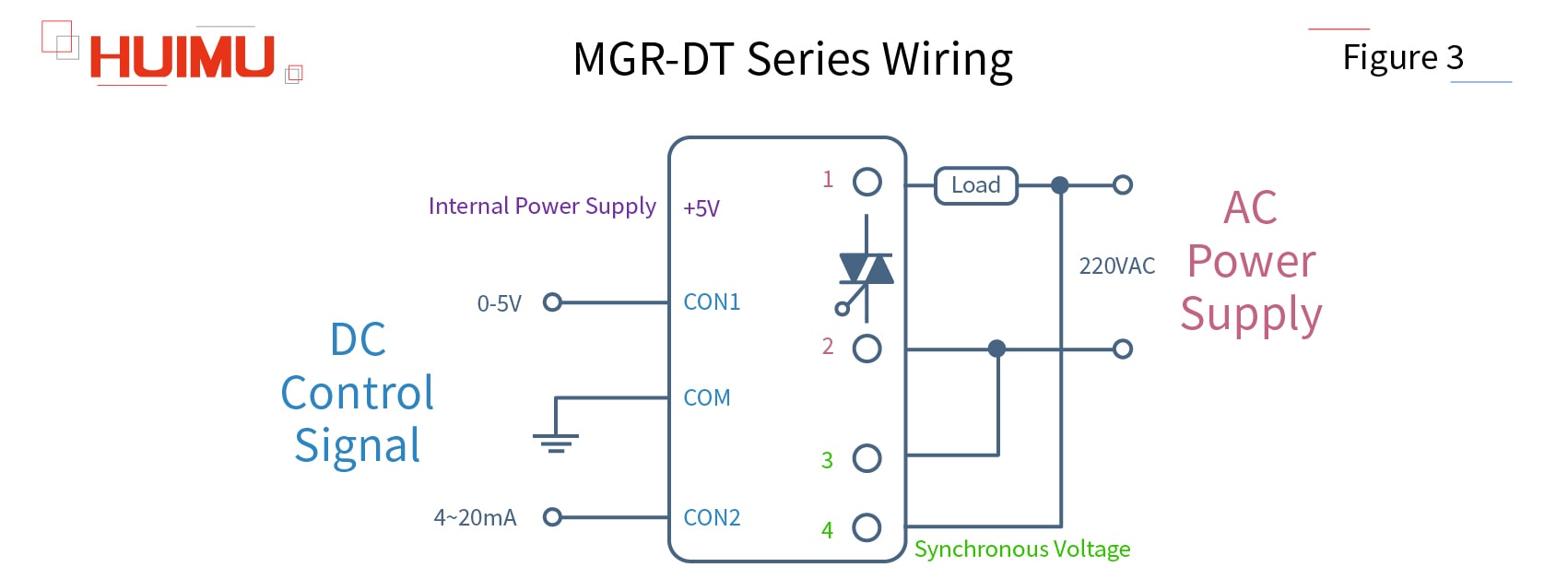
Ports 3 and 4 are connected to the built-in synchronous transformer of the solid-state voltage regulation module. The role of the synchronous transformer is to provide the thyristor in the module with a signal synchronized with the AC voltage of the power supply to ensure that the load voltage can be adjusted accurately without causing output delays and voltage errors. CON1 and CON2 are input ports in automatic control mode; + 5V is the power generated inside the solid-state voltage regulation module, which is used to supply the potentiometer and connected to the high potential side of the potentiometer; COM is the common terminal, and COM will be grounded when choosing the automatic control mode, and COM will be connected to the low potential side of the potentiometer when choosing manual control mode.
The working process of MGR-DT series:
Before talking about how the voltage regulation module works, we need to know that the voltage of Alternating Current (AC) alternates periodically from zero to peak. It is important to know that it is not the instantaneous voltage that does the work on the load, but the effective AC voltage that is thermodynamically equivalent to the DC voltage. Therefore, as long as the working time of the AC voltage in a cycle is changed, that is, its equivalent voltage value is changed, its effective voltage value can be changed. We usually use the thyristor for voltage regulation because it is a controllable component, which means that its conduction capacity can be adjusted by the control signal applied to its control electrode (gate pole). This conduction capacity of the thyristor can be expressed in terms of the conduction angle α on the AC voltage curve. The smaller the conduction angle α, the longer the working time of the thyristor in a cycle, that is, the greater the effective AC voltage; Conversely, the larger the conduction angle α, the shorter the working time of the thyristor in a cycle, that is, the smaller the effective AC voltage. And the control capability of the control signal can be expressed in the form of the control angle θ. The relationship between the control angle θ and the conduction angle α is θ + α = π (180°). Therefore, the larger the control angle, the smaller the conduction angle, that is, the stronger the control signal, the stronger the conduction capacity of the thyristor.
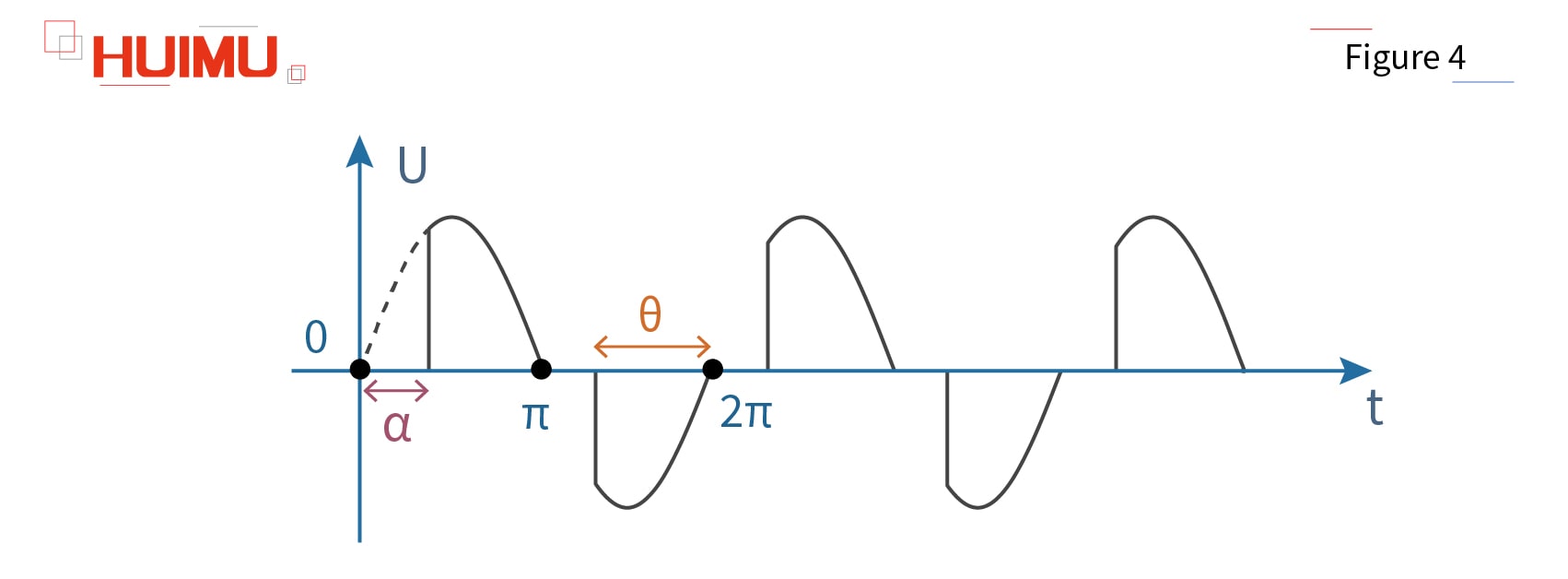
Now we choose CON (0-5VDC) as the control signal, i.e. the control voltage will gradually rise from 0 to 5VDC. Since the start-up voltage (trigger voltage) of the unidirectional thyristor (SCR) is 0.8VDC, if the control voltage is less than 0.8VDC, the thyristor is in the off-state, i.e., the solid-state regulation module is not working. When the control voltage reaches 0.8VDC, even if the SCR starts working, its control angle θ is 0° (i.e., the conduction angle is 180°), so the voltage regulation module does not output any power at this time. When the control voltage is regulated from 0.8 to 5VDC, the control angle rises smoothly from 0° to 180° (i.e., the conduction angle decreases smoothly from 180° to 0°). Theoretically, the larger the control voltage, the larger the SCR output voltage. But in fact, the saturation voltage of the SCR is 4.6VDC, that is, once the voltage reaches 4.6VDC, the SCR will be saturated (the control angle reaches 180°), and its output voltage has reached its maximum value, so its output voltage will not increase until the SCR is broken down, no matter the control voltage continues to rise to 5VDC or even higher.
2.2 The Working Principle of Solid State Rectification Module
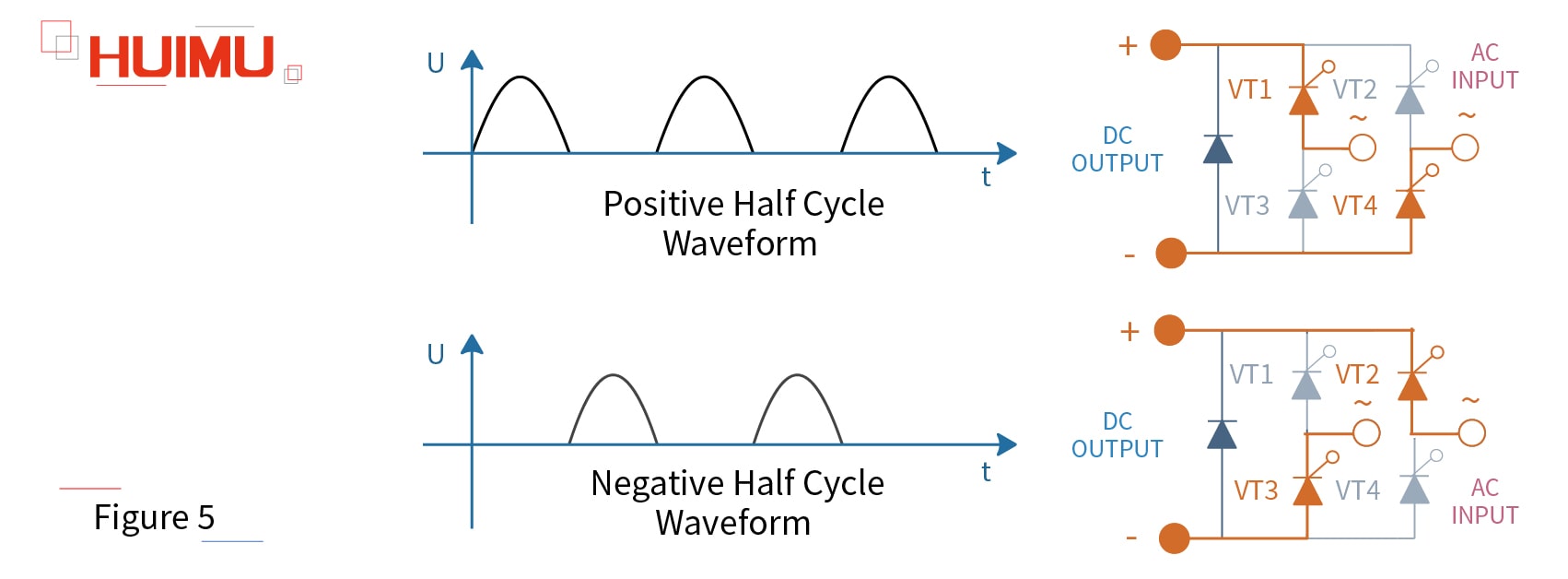
Take MHF series single phase fully control rectification module as an example. The MHF series rectification module contains 4 unidirectional thyristors (SCR), VT1, VT2, VT3, and VT4. Moreover, VT1 and VT4 constitute a pair of bridge arm, and VT2 and VT3 constitute another pair of bridge arm. These two pairs of bridge arms form a full bridge rectifier. When the input voltage U is in the positive half cycle, the flow direction of the current is VT1→R→VT4; when the input voltage U is in the negative half cycle, the flow direction of the current is VT2→R→VT3.
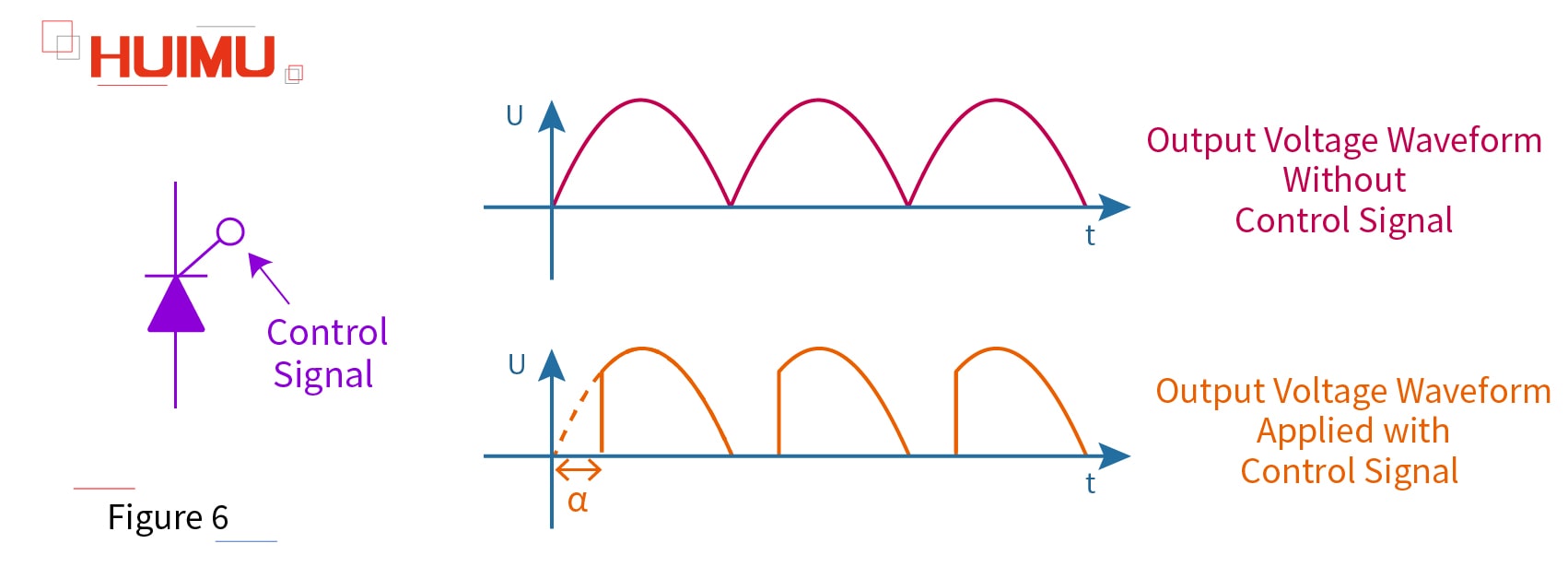
In addition to the rectification function, we can apply a control signal to the control pole (gate pole) of the unidirectional thyristor. By adjusting the conduction angle α of the thyristor, its output waveform and output voltage value can be changed, which is similar to the phase-shift process of voltage regulation module.
§3. How to select the Power Module?
3.1 Voltage Regulator
3.1.1 Single Phase
Standard Potentiometer Type: MGR-R series
Industrial Potentiometer Type: MGR-HVR series
Analog Signal/Continuous Voltage Type: MGR-1VD series
Digital Signal/Pulse Voltage Type: MGR_DV series
External Transformer Type: MGR-EUV series
3.1.2 Three Phase
Basic function: MGR-SCR3_LA series
Multiple function: MGR-SCR_LAH series
3.2 Voltage Regulation Module
3.2.1 Single Phase
Closed-loop Feedback: MGR-DT series
Full-isolation: MGR-DTYF series
3.2.2 Three Phase
Full-isolation: MGR-STY series
3.3 Phase-shift Module
3.3.1 For Solid State Relay
Single Phase: SSR-JK series
Three Phase: SSR-3JK series
3.3.2 For Power Thyristor Circuit
Single Channel/Single Phase: SCR-JKK, TRAIC-JKK series
Dual Channel: SCR-JKK^2 series
Three Channel/Three Phase: SX-JK series
3.4 Solid State Rectifier Relay
Single Phase: MGR-ZK series
Three Phase: MGR-3ZK series
3.5 Solid State Bridge Rectifier
Single Phase: KBPC, QL series
Three Phase: SQL series
3.6 Solid State Rectification Module
3.6.1 Welding Machine Rectification Module
MT, MF, MD series: MT, MF, MD
3.6.2 Solid State Thyristor/Diode Rectification Module
Solid State Thyristor Rectification Module: MTC, MTA, MTK, MTX series
Solid State Diode Rectification Module: MDC, MDA, MDK, MDX series
Solid State Hybrid Rectification Module: MFC, MFA, MFK, MFX series
3.6.3 Full Isolation Single Phase Fully-Controlled Bridge Rectification Module
MGR-DQZ series: MGR-DQZ series
3.6.4 Single Phase/Three Phase Bridge Rectification Module
Single Phase: MDQ series
Three Phase: MDS series
3.6.5 Fully-controlled/Half-controlled Bridge Rectification Module
Single Phase: MFQ, MTF, MHF series
Three Phase: MTQ, MFS, series

Get in touch with us now!
Please take a minute or two to complete this simple form to get reply in 24 hours, thank you!
*Please check the trash box of your mailbox, if you do not receive our email.



